Living with diabetes can be challenging, but with the right approach to diet and exercise, it is possible to effectively manage the condition and maintain a healthy lifestyle. This article provides valuable tips and strategies for individuals looking to manage their diabetes through a combination of proper nutrition and regular physical activity.
May you also like this: Effective Home Workouts without Equipment
Content
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes glucose, a type of sugar. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body does not produce insulin, while type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it. Both types require lifestyle management, including diet and exercise, to keep blood sugar levels in check.
Importance of a Healthy Diet
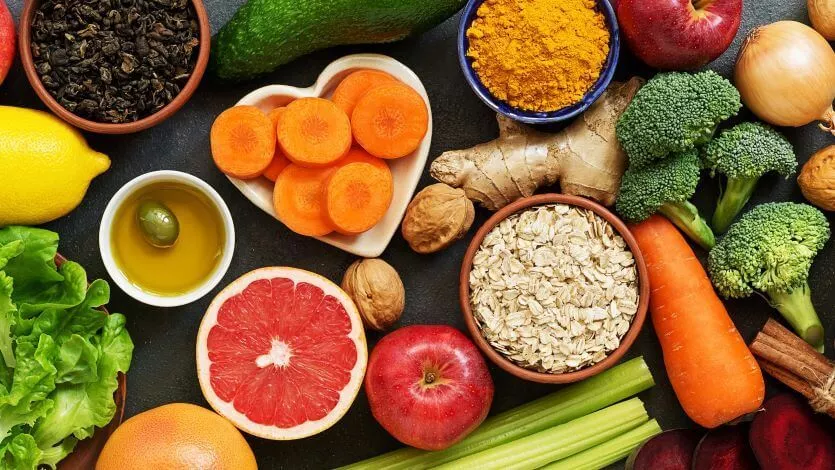

Maintaining a healthy diet is essential for managing diabetes. A well-balanced and nutritious diet can help regulate blood sugar levels, control weight, and prevent complications associated with diabetes. By making conscious food choices, individuals with diabetes can improve their overall health and well-being.
Key Nutritional Guidelines for Diabetics
When it comes to managing diabetes through diet, the following guidelines are crucial:
Carbohydrate Control
Carbohydrates directly affect blood sugar levels, so it’s important to monitor and control their intake. Focus on consuming complex carbohydrates from whole grains, legumes, and vegetables rather than simple carbohydrates found in sugary snacks and processed foods.
Balanced Meals
Create balanced meals that include a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. This helps slow down the absorption of glucose and keeps blood sugar levels stable.
Portion Control
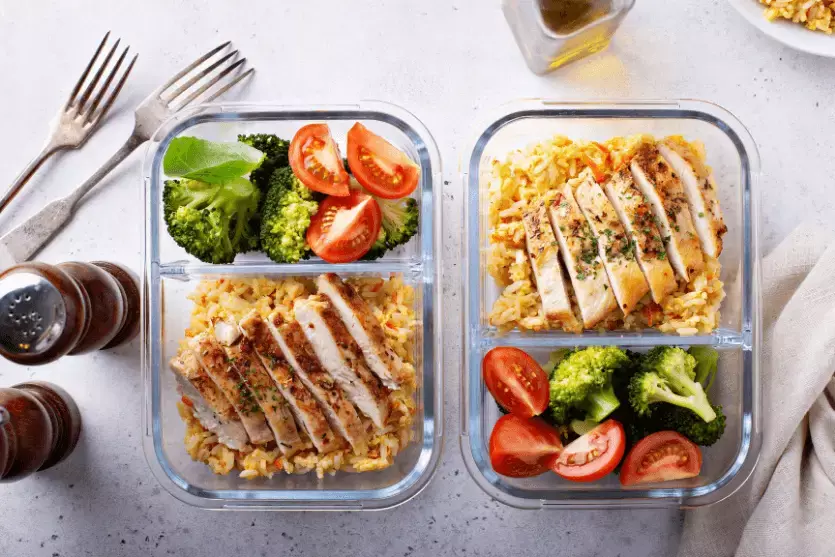

Pay attention to portion sizes to avoid overeating. Use measuring cups or a food scale to ensure accurate portion sizes and keep track of your carbohydrate intake.
Regular Meal Times
Establish regular meal times and spacing between meals to prevent blood sugar spikes and maintain steady glucose levels throughout the day.
Incorporating Exercise into Your Routine
Regular physical activity plays a vital role in diabetes management. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and promotes weight loss. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training exercises twice a week.
Benefits of Exercise for Diabetes Management
Engaging in regular exercise offers numerous benefits for individuals with diabetes:
- Improved blood sugar control
- Increased insulin sensitivity
- Weight management
- Reduced risk of heart disease and other complications
- Enhanced mood and overall well-being
Finding the Right Exercise Routine
Choose activities that you enjoy and can incorporate into your daily routine. Some excellent options include brisk walking, cycling, swimming, dancing, or participating in a fitness class. Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels is essential for effective diabetes management. Use a glucometer to check your levels at home and keep a record of your readings. This information helps you make necessary adjustments to your diet and exercise routine.
Meal Planning and Portion Control
Meal planning is a valuable tool for managing diabetes. Plan your meals ahead of time, incorporating a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This allows for better portion control and helps you make healthier choices.
Making Smart Food Choices
When managing diabetes, focus on nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats into your diet.
Limiting Sugary and Processed Foods
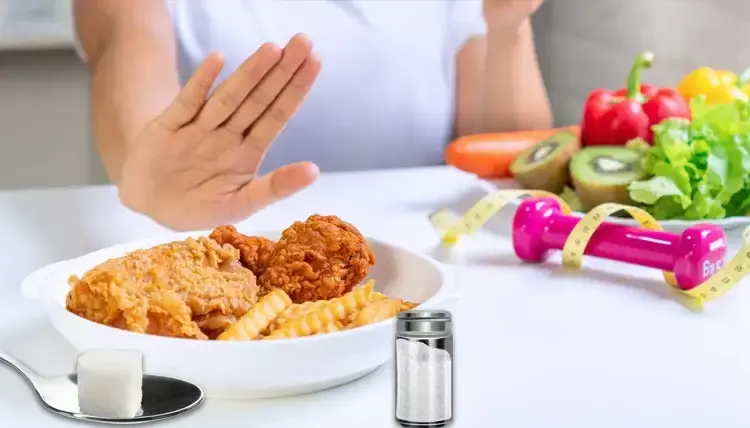

Highly processed foods and sugary snacks can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Limit your consumption of these foods and opt for healthier alternatives such as fresh fruits, unsalted nuts, and whole grain snacks.
Including Fiber in Your Diet
Fiber-rich foods are beneficial for individuals with diabetes as they slow down the absorption of glucose and help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Incorporate sources of fiber such as whole grains, vegetables, legumes, and nuts into your daily meals.
The Role of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. It’s important to learn about the different types of carbohydrates and their effects. Focus on consuming complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index, as they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
Managing Stress and Sleep
Stress and lack of sleep can adversely affect blood sugar control. Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and engaging in activities you enjoy. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
Staying Hydrated
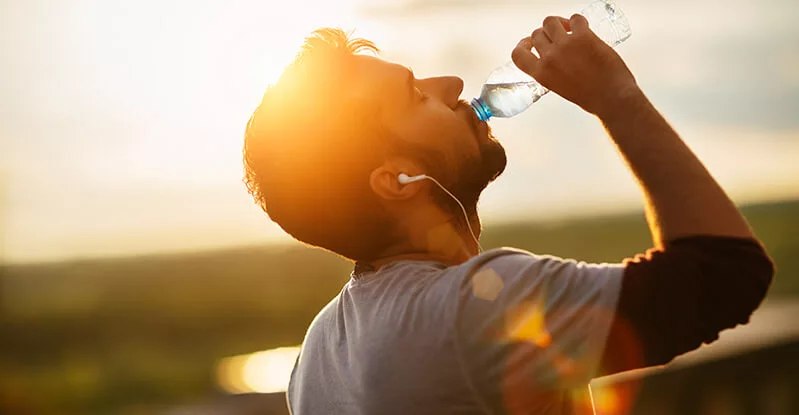

Proper hydration is essential for everyone, especially individuals with diabetes. Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and help regulate blood sugar levels.
Tracking Progress and Seeking Professional Advice
Keep a record of your meals, exercise routine, and blood sugar levels to track your progress effectively. Regularly consult with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian who can provide personalized guidance and support.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes through diet and exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and controlling blood sugar levels. By following the tips outlined in this article, individuals with diabetes can lead fulfilling lives and reduce the risk of complications associated with the condition.
Can I eat carbohydrates if I have diabetes?
Yes, individuals with diabetes can still include carbohydrates in their diet. However, it’s important to focus on consuming complex carbohydrates from whole grains, legumes, and vegetables rather than simple carbohydrates found in sugary snacks and processed foods.
How often should I exercise to manage my diabetes?
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training exercises twice a week. However, it’s best to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized exercise recommendations.
Are there any specific foods I should avoid?
It’s advisable to limit the consumption of sugary and processed foods as they can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Instead, opt for nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
Can stress affect my blood sugar levels?
Yes, stress can impact blood sugar control. Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and engaging in activities you enjoy to help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
When should I seek professional advice for managing my diabetes?
It’s recommended to regularly consult with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance and support. They can help you develop a tailored plan based on your specific needs and goals.

Karen is a health blog author who has been writing about healthy living since 2013. She started her journey by adopting a vegan diet and eating only organic foods, but the more she learned, the more she realized that we should all be eating plant-based diets exclusively. As an expert in nutrition and wellness, Karen blogs to educate readers on how they can live happier and healthier lives through food choices!