An animal-based diet emphasizes whole, nutrient-dense foods derived from animals—like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy—while minimizing or eliminating most plant-based sources. It’s not the same as the carnivore diet; while both prioritize animal products, an animal-based approach allows limited plant intake depending on personal tolerance.
Let’s break down what this diet includes, why it’s gaining popularity, and provide a practical, detailed animal-based diet food list to guide your choices.

Content
What Is an Animal-Based Diet Food List?
An animal-based diet centers around foods that come directly from animals, including meat, organs, dairy, eggs, and animal fats. Unlike restrictive versions like the carnivore diet, animal-based eating may include small amounts of low-toxicity plant foods (like fruits or honey), but these are not essential.
This way of eating draws from ancestral nutrition principles, where early humans thrived on nutrient-dense animal foods. It supports metabolic health, mental clarity, energy levels, and hormonal balance.
Benefits of an Animal-Based Diet
This dietary approach is backed by emerging research and personal success stories. Key benefits include:
- Nutrient Density: Animal foods contain complete proteins, heme iron, B vitamins, omega-3s, and highly bioavailable minerals.
- Improved Digestion: Eliminating anti-nutrients (like oxalates or lectins) can ease bloating and gut discomfort.
- Mental Clarity: The brain thrives on fat and protein—two staples of an animal-based meal plan.
- Hormonal Balance: Fats and cholesterol from animal products support sex hormone production.
- Satiety & Simplicity: High-fat and high-protein meals reduce cravings and promote natural appetite control.
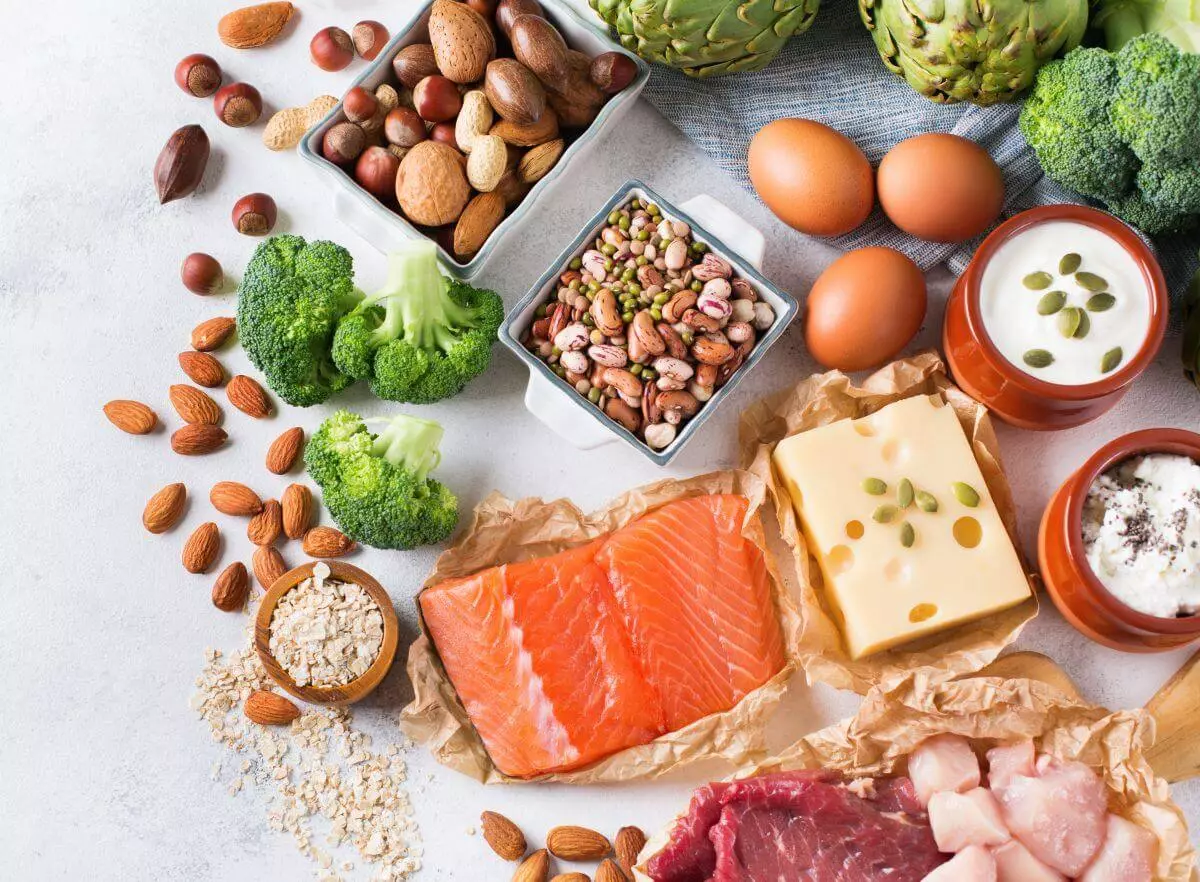
Top 20 Animal-Based Diet Foods
Here’s your ultimate animal-based diet food list, organized by category. These foods form the foundation of a thriving, sustainable animal-based lifestyle:
1. Beef
Grass-fed ribeye, sirloin, and ground beef are nutrient-dense and rich in iron, zinc, and creatine.
2. Lamb
A flavorful red meat high in CLA (conjugated linoleic acid), iron, and selenium.
3. Bison
Lean yet mineral-rich, great for variation without sacrificing nutrition.
4. Chicken
Pasture-raised cuts (especially thighs and wings) offer protein, B vitamins, and healthy fat.
5. Pork
Look for heritage-breed or pasture-raised cuts like pork belly, chops, and tenderloin.
6. Eggs
Whole eggs (especially from free-range chickens) are protein-rich with choline, lutein, and vitamin D.
7. Liver (Beef or Chicken)
Often called nature’s multivitamin—packed with A, B12, folate, and copper.
8. Kidneys
Excellent source of selenium and B vitamins, and a valuable part of nose-to-tail eating.
9. Heart (Beef, Chicken)
Contains CoQ10, essential for heart health and mitochondrial function.
10. Bone Marrow
A creamy, collagen-rich fat source with micronutrients that support joint and brain health.
11. Bone Broth
Slow-simmered bones yield gelatin, collagen, and minerals like calcium and magnesium.
12. Butter
Grass-fed butter provides butyrate, fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K2), and healthy saturated fats.
13. Tallow
Rendered beef fat—ideal for cooking and high in heat-stable saturated fats.
14. Ghee
Clarified butter that’s lactose- and casein-free, rich in fat-soluble nutrients.
15. Raw Cheese
Unpasteurized cheeses (like raw cheddar or gouda) offer probiotics and full-fat nutrition.
16. Heavy Cream
Full-fat dairy that supports ketosis and satiety without added sugars.
17. Salmon (Wild-Caught)
Loaded with omega-3s (EPA & DHA), selenium, and protein.
18. Sardines
Small fish, low in mercury but high in calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids.
19. Shrimp & Shellfish
Low-calorie, high-protein options with iodine, zinc, and selenium.
20. Collagen Peptides
A convenient supplement to support skin, joints, and connective tissues.
Sourcing Animal-Based Diet Food List
To maximize the benefits of your animal-based diet food list, choose high-quality, ethically sourced foods:
- Grass-fed and pasture-raised meats
- Wild-caught seafood
- Raw or minimally processed dairy
- Local farmers, butchers, or online regenerative farms
Avoid meats treated with hormones or antibiotics, and minimize ultra-processed deli meats or factory-farmed products.
Tips for Animal-Based Meal Preparation
- Cook simply: Use low-toxicity animal fats like tallow, butter, or ghee.
- Prioritize variety: Rotate between muscle meats, organs, and seafood.
- Don’t fear fat: It’s a key energy source on this diet.
- Batch-cook: Broths, roasts, and offal-based meals save time and boost nutrient intake.
Final Thoughts
An animal-based diet is more than a trend—it’s a return to what our bodies evolved to thrive on. Whether you’re looking to build muscle, stabilize energy, or optimize mental performance, the animal-based diet food list above offers a nutrient-dense, sustainable roadmap.
By sourcing ethically and preparing meals with intention, you can experience the full benefits of this primal approach to nutrition.
FAQs
Is an animal-based diet the same as carnivore?
No, carnivore is strictly meat and excludes all plant foods. Animal-based may include limited fruits or honey.
Can I eat dairy on an animal-based diet?
Yes, if tolerated. Prioritize full-fat, raw, or minimally processed dairy.

Karen is a health blog author who has been writing about healthy living since 2013. She started her journey by adopting a vegan diet and eating only organic foods, but the more she learned, the more she realized that we should all be eating plant-based diets exclusively. As an expert in nutrition and wellness, Karen blogs to educate readers on how they can live happier and healthier lives through food choices!